In the wake of evolving communication needs during crises like natural disasters, industrial incidents, or pandemics, public bodies have sought more effective ways to transmit alerts to citizens. Recognizing the limitations of legacy warning channels such as radio, TV, or sirens, a paradigm shift occurred in the 2000s. This led to the implementation of mobile-derived technologies, including Location-Based SMS (LB-SMS), for public alerting.
What is Location-Based SMS?
Location-based SMS, or LB-SMS, is a sophisticated method designed to transmit targeted messages to mobile users within specific geographical areas. Unlike traditional SMS, LB-SMS allows for messages predefined by zones, ensuring tailored alerts for vulnerable groups and individuals even after they've left an area.
What are the benefits of Location-Based SMS?
By incorporating LB-SMS into their repertoire, telcos can not only elevate their communication strategies but also actively contribute to public safety initiatives and stay at the forefront of technological advancements in the telecommunications landscape.
Granular communication: LB-SMS enables telcos to customize messages for specific geographic areas, ensuring targeted communication for localized events or promotions.
Omnichannel integration: With an omnichannel approach, telcos can leverage LB-SMS in conjunction with various digital channels such as SMS, social media, and emails. This versatility removes communication boundaries, fostering seamless engagement with users.
Real-time intelligence for local authorities: Telcos can contribute to public safety by providing real-time intelligence based on location data to local authorities. This empowers authorities with critical information for timely and informed decision-making in emergency situations.
Improved positioning accuracy: As 5G continues to evolve, LB-SMS gains from advancements in positioning accuracy, speed, and latency. This is particularly relevant for location-based services, aligning with the growing significance of 5G in enhancing telecommunications.
In conclusion, it should be remembered that LB-SMS provides feedback from the field, fostering immediate situational awareness and enhancing authorities' capabilities in proactive prevention and protection measures.
What are the limitations of Location-Based SMS?
Location-based SMS offers numerous benefits, but it's essential to be aware of its limitations to make informed decisions in its implementation.
Service interruption: During periods of high network congestion, SMS delivery can be delayed or disrupted, leading to potential service interruptions. This can result in critical messages not reaching their intended recipients promptly.
Technical challenges: Implementing effective LB-SMS services requires robust technical infrastructure and integration capabilities. Technical challenges, such as compatibility issues with diverse devices and networks, can hinder seamless deployment.
Message length restrictions: LB-SMS is subject to message length limitations, which can be a drawback when conveying comprehensive information. This restriction contrasts with alternative communication channels, like email or app notifications, which may accommodate longer messages.
Understanding these limitations underscores the need for a balanced approach, which is detailed below.
Maximizing Mass Alerting through the synergy of Cell Broadcast and Location-Based SMS

Depending exclusively on location-based SMS comes with disadvantages, leading experts to endorse a more balanced strategy. Intersec acknowledges the significance of merging location-based SMS with additional technologies, such as Cell Broadcast, to amplify the reach and reliability of public warnings.
Utilizing Cell Broadcast and Location-Based SMS concurrently serves to overcome the inherent limitations each technology encounters independently. This combined approach offers a comprehensive solution, optimizing diverse aspects of public warning systems:
Expanded outreach and efficiency: The combination enables a heightened reach rate, facilitating more effective communication to a wider audience. This collaboration is pivotal in urgent scenarios, guaranteeing immediate and extensive distribution of vital information.
Complementary for adaptable communications: The merging of Cell Broadcast and Location-Based SMS emphasizes the flexibility derived from their complementarity, enabling the choice of the most appropriate alerting technology based on the emergency. Cell Broadcast, with its immediate broadcast capability, is reserved for imminent threats requiring instant action, such as an approaching tsunami. In contrast, LB-SMS provides a more nuanced approach, suitable for situations where information can be conveyed within minutes to tens of minutes, like a flood, ensuring a more targeted broadcast in the specific area.
Incorporating analytical capabilities: Implementing both Location-Based SMS and Cell Broadcast not only empowers Mobile Network Operators (MNOs) to choose the most suitable channel based on the specific situation but also enables them to offer analytics. This strategic collaboration facilitates precise and context-aware communications across the entire crisis lifecycle—before, during, and after the event.
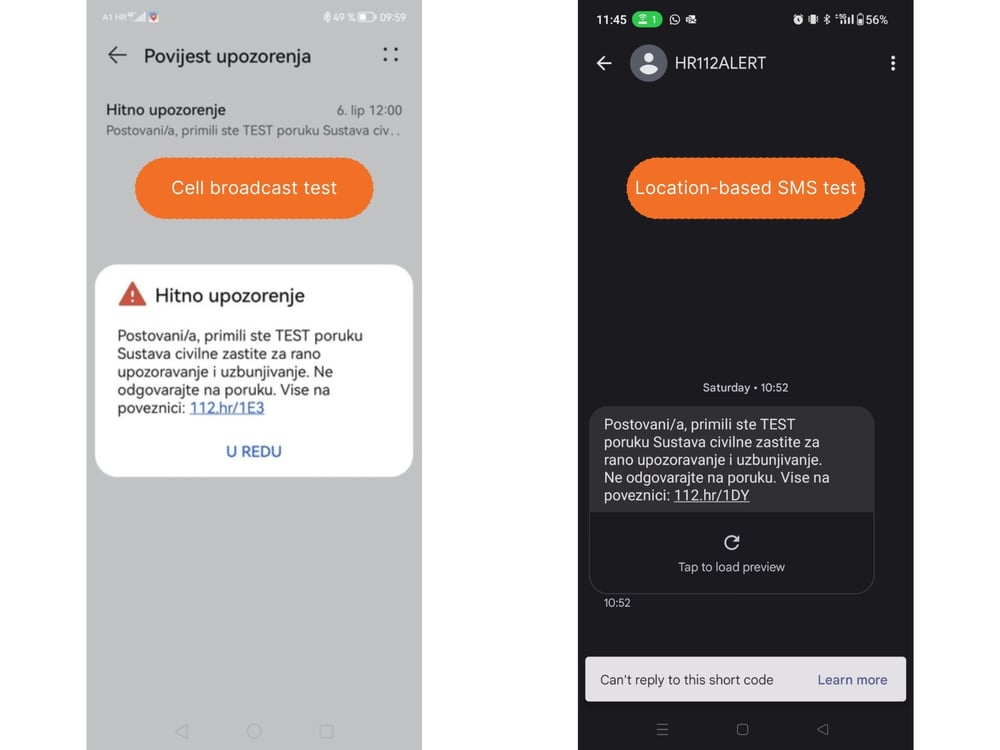
Examples of both Cell broadcast and Location-Based SMS
To learn more about the topic, here are some interesting reads:
→ Whitepaper - Public Warning Systems
→ Whitepaper - Using mobile technologies in public alerting
→ Blog article - Basic Public Warning Systems are expiring soon
→ EENA blog article - FR-Alert, a European reference combining Cell Broadcast and Location-Based SMS
→ Infographics - Which public alerting technologies to use when facing an emergency?
 Location-based SMS for targeted alerts" />
Location-based SMS for targeted alerts" />



.jpg)
.jpg)








.webp)


.webp)




















